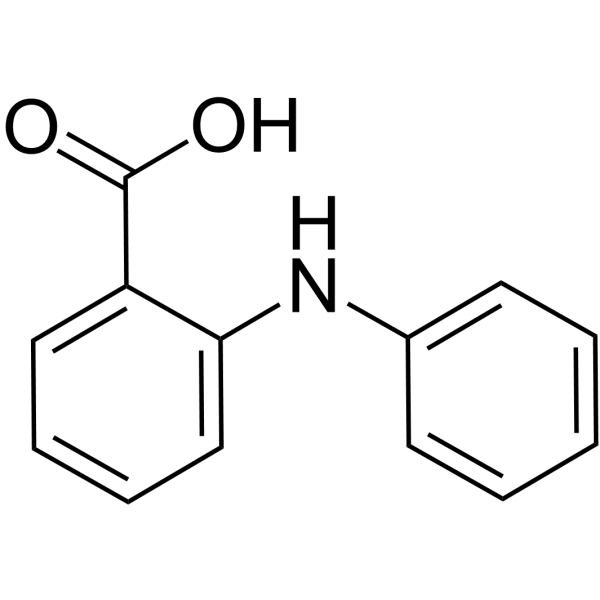
Fenamic acid
CAS No. 91-40-7
Fenamic acid( N-Phenylanthranilic acid | 2-(Phenylamino)benzoic acid | 2-Anilinobenzoic acid | Diphenylamine-2-carboxylic acid )
Catalog No. M27555 CAS No. 91-40-7
Fenamic acid is a chloride channel blocker that causes renal papillary necrosis in rats. Fenamic acid serves as a parent structure for several nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including flufenamic acid, tolfenamic acid, mefenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 50 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 72 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 120 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameFenamic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionFenamic acid is a chloride channel blocker that causes renal papillary necrosis in rats. Fenamic acid serves as a parent structure for several nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including flufenamic acid, tolfenamic acid, mefenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid.
-
DescriptionFenamic acid is a chloride channel blocker that causes renal papillary necrosis in rats. Fenamic acid serves as a parent structure for several nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including flufenamic acid, tolfenamic acid, mefenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid.
-
In VitroFenamic acid (N-Phenylanthranilic acid, NPAA) (2.5 mM; 3 h) inhibits Cl- transportation and blocks 36C1- uptake and efflux in endothelial cells.Fenamic acid exhibits selectivity to AKR1B10 (the tumor-marker) over human AR, and inhibits AKR1B10 with IC50s of 0.76 μM (Flufenamic acid), 1.6 μM (Mefenamic acid), 9.89 μM (Meclofenamic acid), respectively.Fenamic acid (4-16 μg/mL; 72 h) inhibits 50% of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with an MIC50 value from 4 to 16 μg/mL (tolfenamic acid, flufenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid) in a low frequency of resistance. Fenamic acid (2-8 μg/mL; 8 h) reduces the expression of the porinflammatory cytokines (IL-8, IL-6 and IL-?) by infected endocervical cells without (>128 μg/mL; 24 h) inhibition towards commensal Lactobacillus spp. belonging healthy female genital microbiota.
-
In VivoRPA-1 is a biomarker in the detection of collecting duct injury in papillary necrosis in male rats.Fenamic acid (N-Phenylanthranilic acid, NPAA) (350-700 mg/kg/day; o.p.; 4 d, 8 d, and 15 d) causes renal papillary necrosis and increases urinary renal papillary antigen-1 (RPA-1) in rats.Fenamic acid (20 g/0.2 mL; i.p.) shows inhibitory effect against the abdominal constriction induced by acetic acid in mice. Animal Model:Male Wistar Hannover rats (8-10 weeks old; weighting 220-270 g)Dosage:50, 350, or up to 700 mg/kg Administration:Oral gavage; once daily; 7 days or 14 days Result:Increased absolute paired kidney weights (13.8% at 350 mg/kg and 21.2% at 700/500 mg/kg) and relative to body weight (10.5% at 350 mg/kg/day and 20.3% at 700/500 mg/kg/day).Caused minimal papillary necrosis of tip with necrosis, hemorrhage, and inflammation of collecting ducts.Animal Model:Male NMRI mice (weighting 20-25 g); abdominal constriction model (writhing test), induced by acetic acid Dosage:100 g/mL, each mice injected with 20 mL Administration:Intraperitoneal injection; once Result:Showed anti-nociceptive activity and inhibited the abdominal constriction with the maximal inhibition of 96.3% (Mefenamic acid).
-
SynonymsN-Phenylanthranilic acid | 2-(Phenylamino)benzoic acid | 2-Anilinobenzoic acid | Diphenylamine-2-carboxylic acid
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetChloride Channel
-
RecptorApoptosis
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number91-40-7
-
Formula Weight213.236
-
Molecular FormulaC13H11NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 125 mg/mL (586.22 mM)
-
SMILESOC(=O)c1ccccc1Nc1ccccc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Iskandar K, et al. Synthetic Lethality of a Novel Small Molecule Against Mutant KRAS-Expressing Cancer Cells Involves AKT-Dependent ROS Production. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 May 10;24(14):781-94.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Anestan
Halothane is an inhalational general anesthetic. It is the only inhalational anesthetic containing bromine.
-
CLP257
CLP257 (CLP-257) is a potent, selective K+-Cl- cotransporter KCC2 activator with EC50 of 616 nM.
-
Brucine sulfate hept...
Brucine is an alkaloid that acts as an antagonist at glycine receptors and paralyzes inhibitory neurons.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


